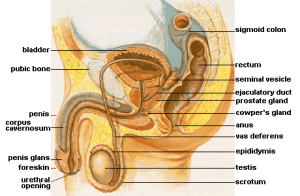
Penile cancer in the United States is quite rare. It occurs in less than 1 in 100,000 men and accounts for less than 1 percent of cancers in men in the United States. It is more common in areas of Asia, African, and South America. The most common type of penile cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, which usually forms on or under the foreskin. Signs and symptoms of penile cancer may include discharge, redness, irritation, or sores, a lump on the penis, or bleeding.
Key statistics for penile cancer:
- It is estimated that for 2015 in the United States, there will be about 1,820 new cases of penile cancer diagnosed and about 310 deaths from penile cancer.
- Penile cancer is most common in parts of Asia, Africa, and South America. It accounts for up to 10 percent of cancers in men in these areas.
- Penile cancer is rare in North America and Europe. It occurs in less than 1 man in 100,000 and accounts for less than 1 percent of cancers in men in the United States.
Risk factors for penile cancer:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Men who are uncircumcised
- Having multiple sex partners
- Being aged 60 or older
- Having poor personal hygiene
- Smoking
- Having phimosis (a condition in which the foreskin of the penis cannot be pulled back over the glans)
There are a number of tests and procedures used to determine whether penile cancer is present. If penile cancer is suspected, your doctor may perform a physical examination to check for signs of penile cancer such as discharge, redness, irritation, or sores, a lump on the penis, or bleeding. Your doctor will also assess your past medical history. Your doctor may also perform a penile biopsy to remove tissue which is sent to a pathologist for analysis.
There are three types of biopsies that may be performed: a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, an incisional biopsy, or an excisional biopsy. A fine-needle aspiration biopsy is the removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle. An incisional biopsy is the removal of part of a lump or a sample of tissue that doesn’t look normal. And an excisional biopsy is the removal of an entire lump or area of tissue that doesn’t look normal.
The three types of standard treatment for penile cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. There are also new types of treatment that are being tested in clinical trials which include biologic therapy, radio-sensitizers, and sentinel lymph node biopsy followed by surgery.




Most cases of cancer recorded are on women since women have relatively more parts of the body that cancer can develop into. Prostate cancer was the only type of cancer I know that hits men. This is actually my first time hearing of penile cancer. And thanks to you, David, I was able to understand the repercussions of it. Although only a few can acquire this kind of cancer, it is still alarming since its targeting probably the most vulnerable part of a male’s body. Fortunately, like all types of cancer that have been discovered, this one already has a cure. But the best cure out there is prevention. So thanks, David, for providing this very informative article.